WebSphere Naming architecture
WebSphere Application Server
name servers are an implementation of the CORBA
CosNaming interface. WebSphere Application Server provides a JNDI implementation
that you can use to access CosNaming name servers through the JNDI interface.
CosNaming provides the server-side implementation and is where the name space is
stored. JNDI essentially provides a client-side wrapper of the name space stored
in CosNaming, and interacts with the CosNaming server on behalf of the
client.
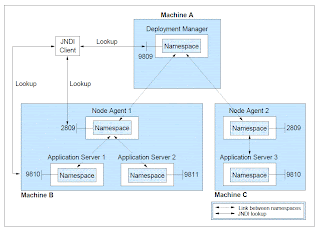
I copied this diagram from System Management Handbook red book, that explains the Naming service architecture
I copied this diagram from System Management Handbook red book, that explains the Naming service architecture
wsadmin script to print namespace
wsadmin script to print namespace
You can dump
namespace of a managed process i.e. either DMGR, NodeAgent or Server using
dumpNamespace tool. Other option is to use the following wsadmin script
The
def printNameSpace(processname):
print "Printing name space for " + processname
nameserver =AdminControl.queryNames("*:*,type=NameServer,process="+porcessname)
print AdminControl.invoke(nameserver,"dumpServerNameSpace",'["-report long"]')
printNameSpace('dmgr')The
printNameSpace command takes name of
the process as argument and generates dump which is same as the output of the
dumpNameSpace for that process JNDI dumpNameSpce
The
dumpNameSpace tool is used to dump the contents of a name space accessed through
a name server. The tool can be run from the websphere_root/AppServer/bin
directory in a command
JNDI dumpNameSpce
The
dumpNameSpace tool is used to dump the contents of a name space accessed through
a name server. The tool can be run from the websphere_root/AppServer/bin
directory in a command

Important Note: The dumpNameSpace command line utility does not dump java: or local: name spaces. These name spaces, along with the server: name space, can be dumped using a Managed Bean (MBean) called NameServer

Important Note: The dumpNameSpace command line utility does not dump java: or local: name spaces. These name spaces, along with the server: name space, can be dumped using a Managed Bean (MBean) called NameServer
Naming service feature
The following
are features of a WebSphere Application Server V6 name space
that remain unchanged from WebSphere Application Server V5:
that remain unchanged from WebSphere Application Server V5:
- Distributed name space: For additional scalability, the name space for a cell is distributed among the various servers. The deployment manager, node agent, and application server processes all host a name server. The default initial context for a server is its server root. System artifacts, such as EJB homes and resources, are bound to the server root of the server with which they are associated.
- Transient and persistent partitions: The name space is partitioned into transient areas and persistent areas. Server roots are transient. System-bound artifacts such as EJB homes and resources are bound under server roots. There is a cell persistent root, which can be used for cell-scoped persistent bindings, and a node persistent root, which can be used to bind objects with a node scope.
- Federated name space structure: A name space
is a collection of all names bound to a particular name server. A name space can
contain naming context bindings to contexts located in other servers. If this is
the case, the name space is said to be a federated name space, because it is a
collection of name spaces from multiple servers. The name spaces link together
to cooperatively form a single logical name
space.
The name space for the WebSphere Application Server V6 cell is federated among the deployment manager, node agents, and application servers of the cell. Every server process hosts a name server. All name servers provide the same logical view of the cell name space, with the various server roots and persistent partitions of the name space being interconnected by means of the single logical name space. - Configured bindings: Administrators can configure bindings into the name space. A configured binding is different from a programmatic binding in that the system creates the binding every time a server is started, even if the target context is in a transient partition.
- Support for CORBA Interoperable Naming Service (INS) object URLs WebSphere Application Server contains support for CORBA object URLs (corbaloc and corbaname) as JNDI provider URLs and lookup names

No comments:
Post a Comment